Fermented foods have been a staple in many cultures for centuries, not only for their unique flavors but also for their incredible health benefits. From kimchi in Korea to yogurt in Greece, these foods are packed with probiotics, essential nutrients, and enzymes that support digestion, boost immunity, and improve overall well-being. Incorporating fermented foods into your diet can be a simple and delicious way to enhance gut health and maintain a balanced lifestyle.

1. What Are Fermented Foods?
Fermentation is a natural process where beneficial bacteria and yeasts break down sugars in food, producing organic acids, gases, and sometimes alcohol. This process enhances the food’s nutritional profile, preserves it for longer periods, and creates probiotics that support gut health. Some of the most popular fermented foods include:
- Yogurt – A probiotic-rich dairy product that supports digestion and bone health.
- Kimchi and Sauerkraut – Fermented vegetables that provide fiber, vitamins, and gut-friendly bacteria.
- Kefir – A tangy, drinkable yogurt alternative with high probiotic content.
- Kombucha – A fermented tea that contains beneficial enzymes and organic acids.
- Miso and Tempeh – Fermented soy-based foods that are excellent sources of protein and probiotics.

2. Improves Gut Health and Digestion
One of the most significant benefits of fermented foods is their impact on gut health. They contain live probiotics, which help restore and maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. This can:
- Aid in digestion by breaking down food more efficiently.
- Reduce bloating and gas by improving gut flora.
- Help manage conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Enhance nutrient absorption, ensuring your body gets the most out of your food.

3. Strengthens the Immune System
A large portion of the immune system resides in the gut, meaning a healthy digestive system is crucial for overall immunity. Probiotics found in fermented foods help:
- Strengthen the gut lining, preventing harmful bacteria from entering the bloodstream.
- Reduce inflammation, which can lower the risk of chronic diseases.
- Increase the production of natural antibodies, helping the body fight off infections.

4. Supports Mental Health and Mood
Emerging research suggests that gut health is closely linked to brain health. The gut-brain connection, also known as the “gut-brain axis,” means that probiotics can influence mood, anxiety, and even cognitive function. Fermented foods may:
- Reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Improve mental clarity and focus.
- Support the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood.
5. Promotes Heart Health
Certain fermented foods have been linked to improved heart health by helping regulate cholesterol levels and blood pressure. For example:
- Kefir and yogurt contain probiotics that can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol.
- Fermented soy products like miso may contribute to lower blood pressure and reduced risk of heart disease.
- Kimchi and sauerkraut contain antioxidants and fiber, which promote cardiovascular health.
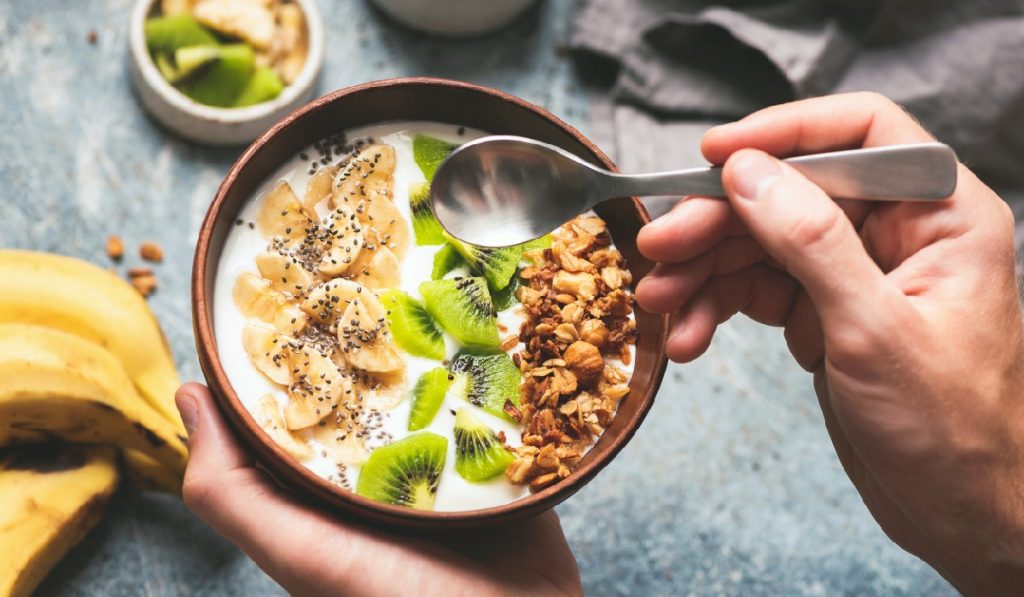

6. How to Incorporate More Fermented Foods into Your Diet
Adding fermented foods to your daily meals is easy and can enhance both flavor and nutrition. Here are some simple ways to enjoy them:
- Start your morning with a bowl of yogurt topped with fresh fruit and nuts.
- Use sauerkraut or kimchi as a flavorful side dish with meals.
- Drink a glass of kombucha instead of soda for a probiotic boost.
- Add miso to soups or dressings for extra depth of flavor.
- Snack on tempeh or include it in stir-fries for a protein-rich meal.

